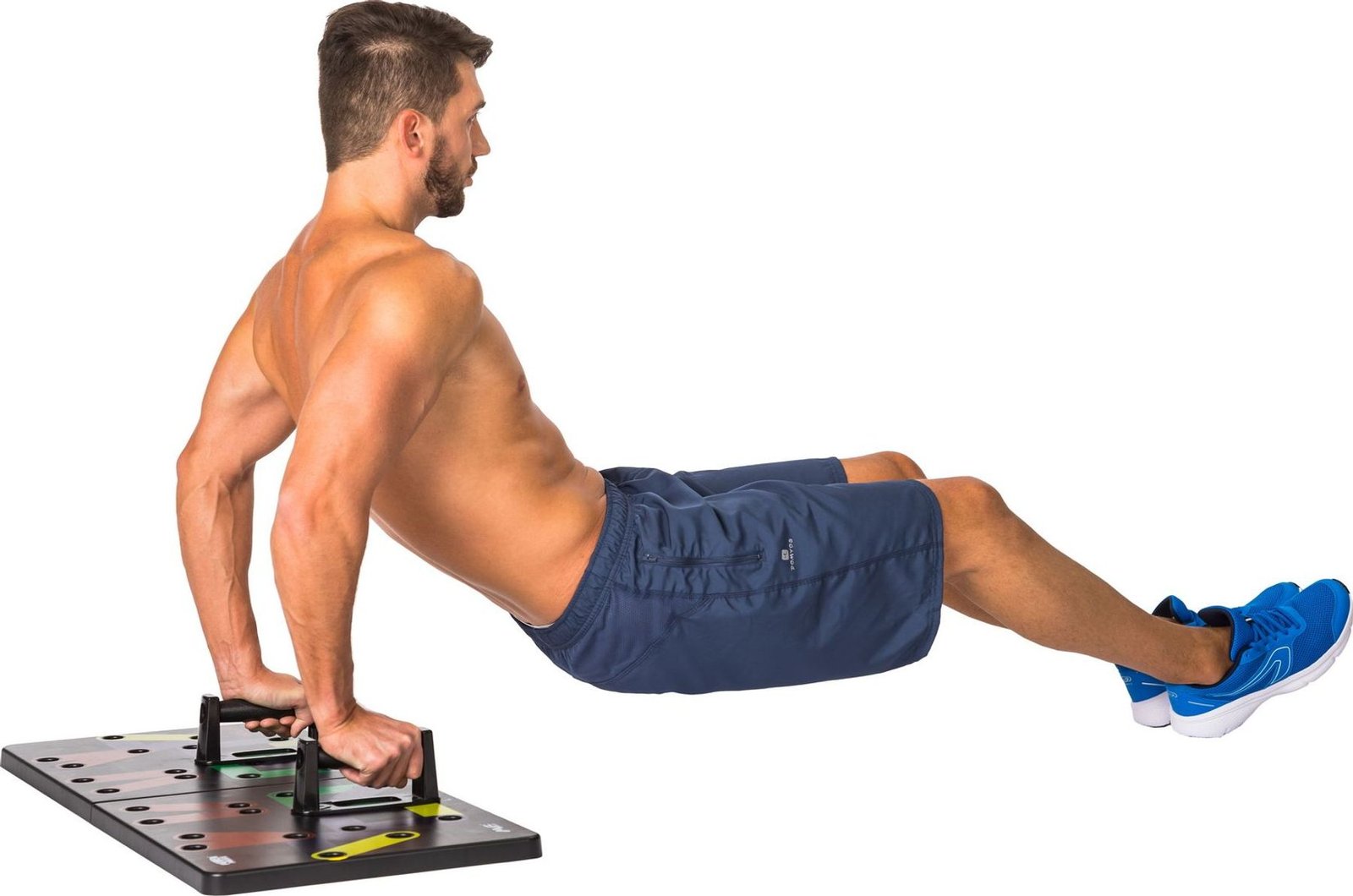
The Best 5 Upper Cross Syndrome Exercises for Postural Health
Upper Cross Syndrome Exercises (UCS) is a widespread postural disease characterized by tightness inside the top returned and chest with weak points in the neck and mid-lower back muscle groups. Addressing Upper Cross Syndrome Exercises is vital for enhancing posture, reducing pain, and improving normal physical health. This article explores the pinnacle 5 Upper Cross Syndrome Exercises, each tailored to fight the imbalances due to Upper Cross Syndrome Exercises. This comprehensive guide focuses on powerful and safe exercises to optimize postural health.
Best 5 Upper Cross Syndrome Exercises
1. Chest Stretch
The Chest Stretch is an important exercise for alleviating the tightness within the chest muscle groups, a not unusual symptom of Upper Cross Syndrome Exercises this tightness regularly outcomes from prolonged sitting or bending forward, leading to a hunched posture. To perform the Chest Stretch, stand in a doorway and function your forearms against the frame, elbows at about shoulder height. Lean ahead till a chilled stretch is felt within the chest muscle groups. Hold this role for 15-30 seconds, ensuring you breathe deeply. This upper cross syndrome exercises prolongs the pectoral muscles, promoting an extra open chest and an upright posture, which is critical in counteracting the outcomes of Upper Cross Syndrome Exercises.

Improved Posture: Regularly appearing the chest stretch allows open the chest muscle groups, regularly shortened and tightened in Upper Cross Syndrome Exercises. This stretching leads to a greater upright and open posture, counteracting the slouching addiction.
Enhanced Breathing: Tight chest muscle groups can restrict lung growth, impacting respiration. Chest Extension considers more profound, more efficient respiration by developing the thoracic despair.
Lowering Your Risk of Musculoskeletal Pain: Delayed chest snugness can activate torment and distress.
Improved Shoulder Mobility: As the chest muscular tissues are stretched and lengthened, shoulder mobility improves, making it less difficult to perform overhead activities without pressure.
2. Neck Retractions
Neck Retractions target weakened neck muscle groups, particularly the deep cervical flexors. This workout allows accurate ahead head posture, which is a feature of Upper Cross Syndrome Exercises.
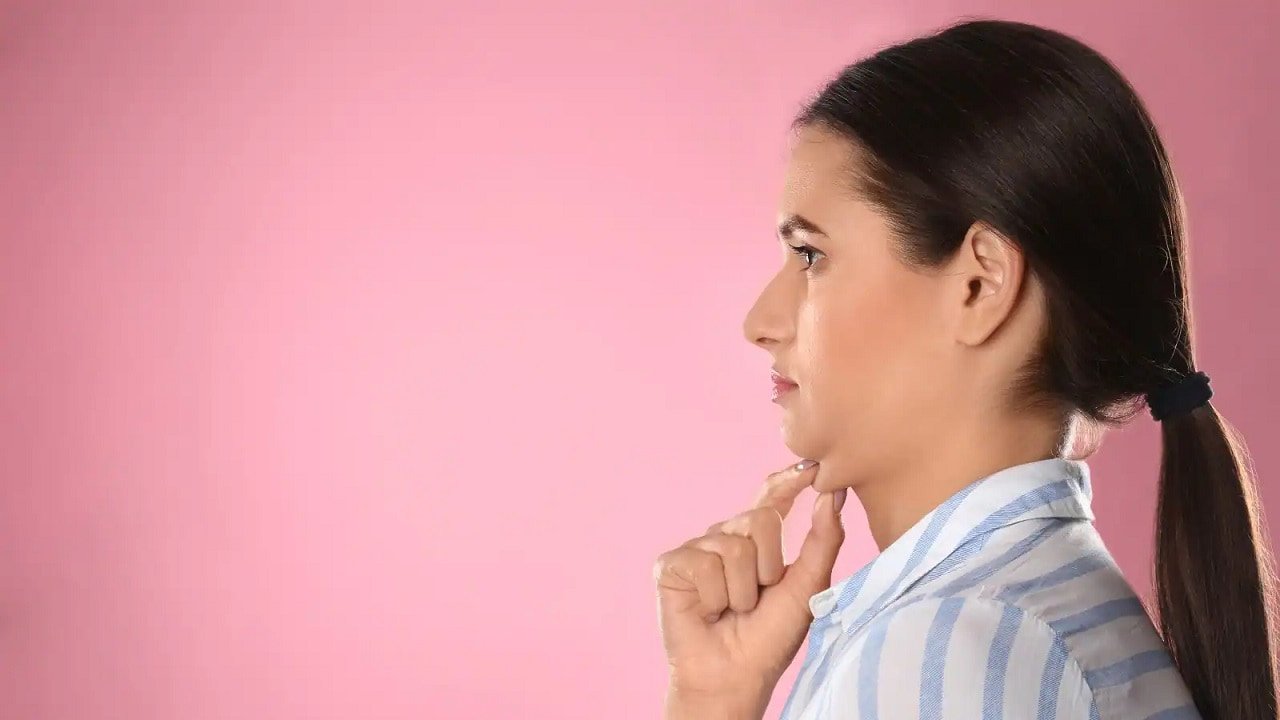

To perform:
Sit or stand along with your spine in a neutral position.
Gently pull your head instantly back, keeping the chin tucked in, and grow a double chin. This function ought to be held for five seconds before releasing.
Repeat the exercise in 10 instances.
Regular neck retractions improve the neck muscle tissue, supporting higher alignment and decreasing neck stress.
Correcting Forward Head Posture: Neck retractions are critical in restoring the ahead head posture, a hallmark of Upper Cross Syndrome Exercises. This realignment is essential for reducing stress on the cervical backbone.
Decreased Neck Pain and Tension: These Upper Cross Syndrome exercises help lessen continual neck pain and tension, common signs of Upper Cross Syndrome Exercises, by strengthening the neck muscle groups.
Enhanced Concentration and Reduced Headaches: Proper neck alignment can reduce anxiety headaches and improve concentration by way of alleviating stress on the neck and head.
Better Upper Body Kinetics: Neck retractions contribute to an extra-balanced head-neck alignment, improving universal upper body kinetics and motion efficiency.
3. Thoracic Extension
Thoracic Extension physical activities intend to decorate mobility within the top returned, basically focusing on the thoracic backbone, to counteract the stiffness and rounding frequently visible in Upper Cross Syndrome Exercises. People generally use a foam roller to carry out this exercise. Lie for your lower back with the froth curler located under your top back. Support your head along with your arms and gently arch your lower back over the roller, transferring it along the duration of your upper backbone. This exercise must be executed for 5-10 minutes daily to loosen tight muscle groups and enhance spinal flexibility effectively.
Improved Spinal Health: Thoracic Extension exercises an awareness of mobilizing the thoracic backbone, lowering the threat of spinal degeneration, and improving overall spinal health.
Alleviation of Upper Back Pain: These Upper Cross Syndrome Exercises assist in stretching and reinforcing the top lower back muscle tissues, relieving aches and stiffness associated with UCS.
Enhanced Lung Capacity: Thoracic Extension sports can also boost lung energy by starting in the chest region, benefiting breathing fitness.
Better Overall Body Alignment: Regular exercise facilitates accurate, rounded top posture, which leads to better alignment of the complete body.
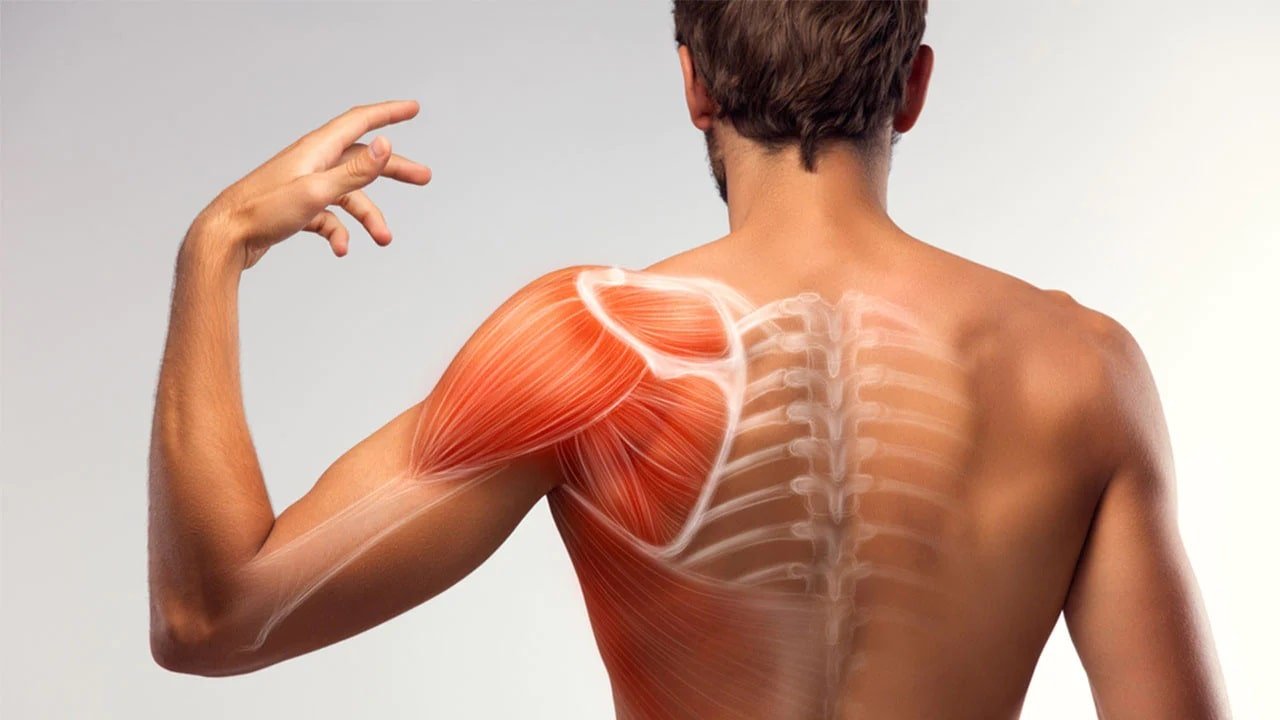
4. Scapular Retraction
Scapular Retraction exercises are important for strengthening the muscle mass across the shoulder blades, which might often be weakened because of UCS. This exercise involves sitting or standing with your palms relaxed at your sides. Draw your shoulder blades back and down as though trying to pinch them together. Hold this position for five seconds, after which relax. Performing 10-15 repetitions of this exercise helps improve scapular balance and alignment, which is critical for keeping a healthful top back and shoulder posture.
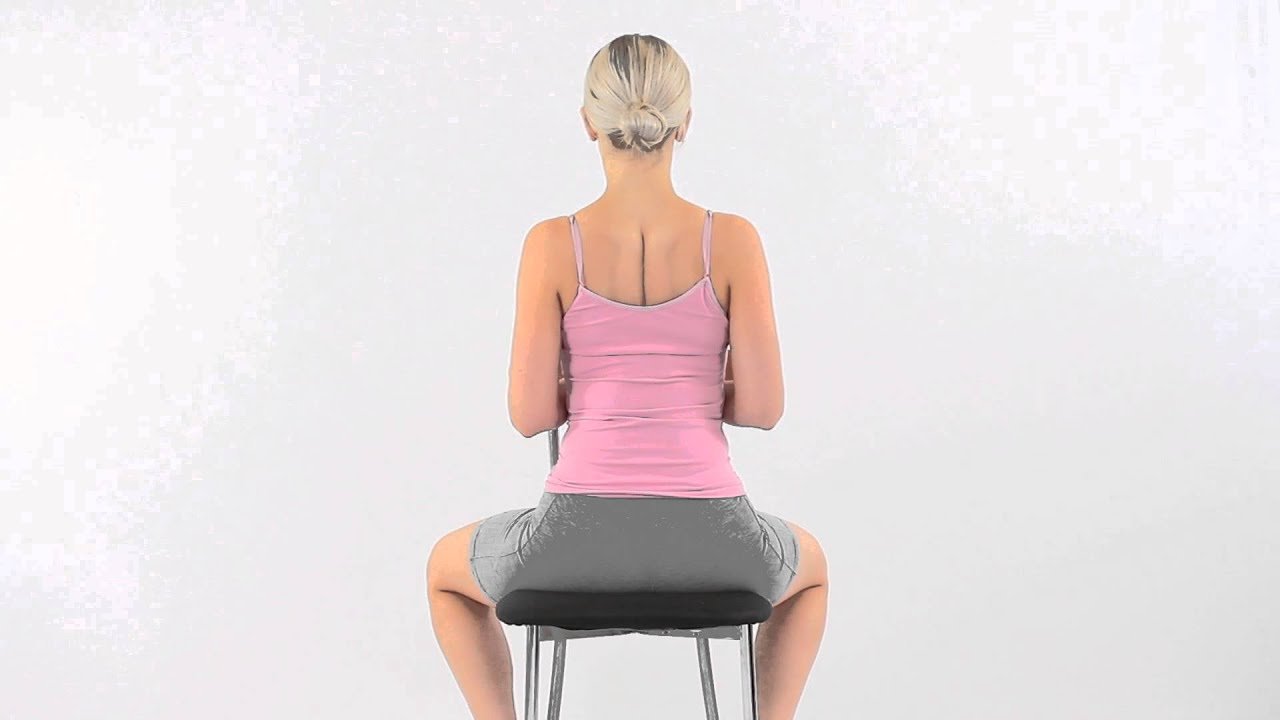

Strengthened Upper Back Muscles: Scapular retraction physical games are essential in retaining the muscular tissues between the shoulder blades, which are often weakened in UCS.
Reduced Shoulder Pain: Strengthening these muscle masses stabilizes the shoulder joint, decreasing the threat of shoulder pain and accidents.
Improved Posture: Regular exercise of scapular retractions promotes a more aligned and upright posture, that’s essential for common spinal health.
Enhanced Athletic Performance: Stronger scapular muscle mass can improve overall performance in sports and activities that require top-frame electricity and balance.
5. Shoulder Blade Squeeze
The shoulder blade squeeze is a version of the scapular retraction that focuses on the rhomboid and decreases trapezius muscles. Squeeze your shoulder blades collectively and downwards, keeping your neck relaxed. Sit or stand with elbows bent and forearms parallel to the floor. Squeeze your shoulder blades collectively and downwards, keeping your neck comfortable. Hold this function for 5 seconds and then launch. Repeat these ten instances. This exercise aids in correcting the rounded shoulder posture and strengthens the upper again muscular tissues, that’s critical for a balanced top body posture in UCS.
Corrected Rounded Shoulder Posture: The goal of this exercise is to correct the rounded shoulder posture normal in UCS, promoting higher shoulder alignment.
Reduced Tension in Neck and Shoulders: Regular practice allows the tension built up in the neck and shoulders, which is not unusual in UCS, to be eased.
Improved Upper Body Appearance: Strengthening and realigning the shoulder blades contribute to a greater aesthetically appealing top body posture.
Enhanced Functional Capabilities: Stronger shoulder and top returned muscle tissue enhance functional capabilities in daily activities, lowering the threat of injury and strain.
Conclusion
The benefits of physical games for Upper Cross Syndrome Exercises are multifaceted, addressing both the bodily and psychological components of well-being. The strong irregular characteristics and postural issues associated with UCS contribute to a preferred development in personal satisfaction. The customary and predictable acts of those sports are vital to receiving their general rewards, prompting a greater adjustment and torment-free.
FAQs For Best 5 Upper Cross Syndrome Exercises
Can Upper Cross Syndrome be cured completely?
Yes, with consistent exercising, exact ergonomics, and lifestyle modifications.
How long does it take to see improvement with sporting events?
Typically, within some weeks of everyday exercise.
Are there any sports to keep away from with Upper Cross Syndrome?
Avoid heavy overhead lifting and activities that stress the neck and shoulders.






